
Menu

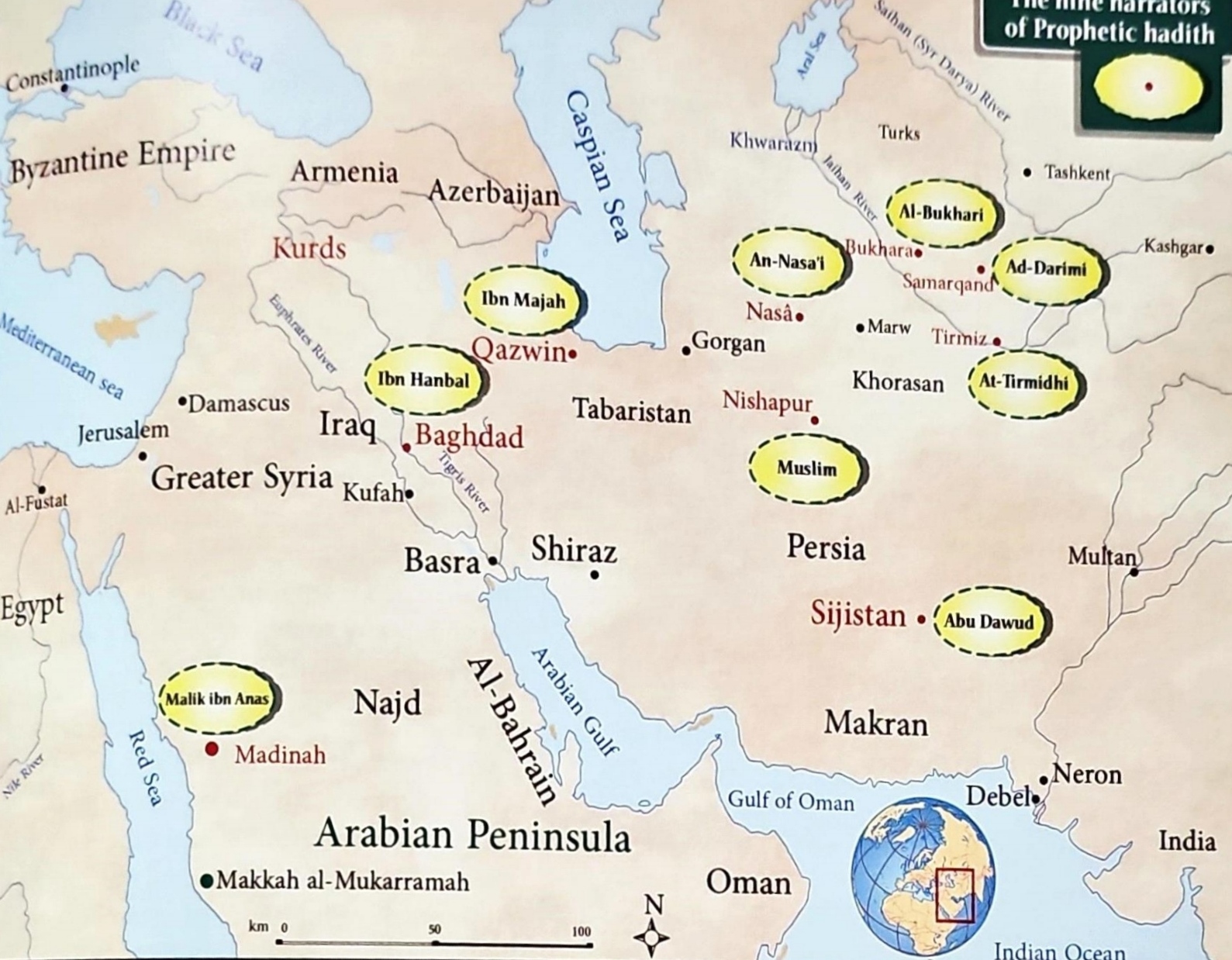
The Major Hadith Compilations and Their Scholars (Sahihayn & 'Sihah Sittah')
First written on 29 July 2023 | 10 Muharram 1445 AH | Last Updated on 30 July 2023 at 3:20 am.
Born: {13th} Shawwal 194 AH (c. 21 July 810 CE) in Bukharah (in present day Uzbekistan).
Died: Eve of Eid-ul-Fitr 256 AH (ie 1st Shawwal 256 AH, c. 1 Sept 870 CE) at Khartank near Samarqand (in present day Uzbekistan). He lived during period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full name: Abu Abdullah Muhammed ibn Ismail ibn Ibrahim ibn al-Mughirah ibn Bardizbah al-Jufi Mawlahum.
Brief Bio:
Imam al-Bukhari started travelling extensively in pursuit of hadith in 210 AH. Among places he travelled to for Hadith are Hijaz (for six years), Shaam (Syria), Egypt, Mesopotamia, Basrah, Kufah and Baghdad. Imam al-Bukhari was well known for his proverbial memory. He was also very pious and of a great character.
Major Works:
(1) Sahih al-Bukhari: The most authentic of all books of Hadith. Al-Bukhari intended to collect only authentic hadith and those that are of very high level of authenticity. Contains about 7563 hadith including repetitions and parts of hadith spread across its 97 chapters (Kitab). Chapter headings include deeply thought, understood and expertly deduced rulings or benefits from the hadith contained in the chapter.
(2) at-Tarikh al-Kabir and other such volumnous large books with biographies of narrators with respect to their authenticity as narrators of hadith.
(3) al-Adab al-Mufrad: A collection of hadith about Islamic character, manners and etiquettes.
(4) Kitab Raf' al-Yadayn (Book on Raising the Hands): In this booklet, Imam Bukhari collected many narration of the Prophet and of the Companions each showing that raising the hands to the ears before and after Ruku in Prayer is part of the way of the Prophet's Prayer.
(5) Kitab Khalq Af'aal al-Ebaad: Booklet with hadith that show the teachings of Islam about the belief in the sixth pillar of Iman, ie Belief in Qada and Qadar. The book shows that the actions of human beings are created by Allah and performed by human beings. Imam Bukhari authored this book to show to refute wrong and distorted beliefs that were being propagated by a group of people in those days.
Born: 204 AH ({or 206} / c. 815 CE) in Nisapur (presently in Iran).
Died: 261 AH (aged 57) (c. 875 CE) in Nisapur. Lived during the period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full Name: Abu-l-Hussain Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj ibn Muslim al-Qushairi an-Naispuri.
Brief Bio:
Imam Muslim travelled extensively in pursuit of Hadith, including to Hijaz, Shaam (Syria), Iraq, and Egypt. When Imam al-Bukhari visited Naisapur, Imam Muslim kept company of him learning from him and was a close student of Imam al-Bukhari.
Major Works:
Sahih Muslim: The second most authentic collection of hadith of the Prophet Muhammed. Imam Muslim compiled this book as a collection of only authentic hadith. There are about 3033 hadith with about 7500 narrations of those hadith, later marked by Nawawi as 56 chapters following the Introduction. In the Introduction, Imam Muslim elucidated many aspects of the knowledge of hadith collection and authenticity supported by hadith. These hadith in the Introduction are not classed as part of the Sahih Muslim with its high level of authentic hadith, rather they are considered as part of its Introduction. Typically in each chapter, Imam Muslim placed the most authentic chain of narration in the beginning and followed it with other chains of the same hadith with varying level of authenticity but with some added benefit to be brought to the reader. Unlike Imam Bukhari who wrote chapter headings with understanding of hadith in that chapter, Imam Muslim did not write any chapter headings nor delineate the chapters with any markers. However, latter day Scholars, including Nawawi, wrote and inserted chapter headings to those hadith along with explanation and commentary.
Born: 202 AH (c. 817-818 CE) in Sijistan (in present day border region of Iran and Afghanistan).
Died: 275 AH (c. 889 CE) in Basrah, Iraq (aged 73). Lived during the period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full Name: Abu Dawud Sulaiman ibn al-Ash'ath ibn Ishaq al-Azdi as-Sijistani.
Brief Bio:
Like the other great Scholars of Hadith, Imam Abu Dawud also travelled extensively in oursuit of Hadith from their narrators. Among places he travelled to include Iraq, Shaam (Syria), Egypt and Khorasan. Abu Dawud learnt from the esteemed great Scholar and Imam Ahmed ibn Hanbal, who was also a teacher of Imams Bukhari and Muslim. Abu Dawud became a great Scholar of Hadith and Islam in general, was known for his piety as with other great Scholars, and also known for his expertise in fiqh (understanding) and memory.
Major Works:
(1) Sunan Abu Dawud: This is one of the six most renowned collections of Hadith and it is a great source of hadith of ahkam/fiqh. Sunan Abu Dawud has 43 Chapters, together containing about 5274 Hadith. Imam Abu Dawud organised the chapters of this book according to fiqh book chapters arrangement with a focus on fiqh of hadith as seen from the chapter headings that the author placed in it. Imam Abu Dawud did not intend to collect only authentic hadith in this book, rather to collect hadith to do with fiqh so long as they were suitable to he considered independently on their own or along with other narrations, hence Abu Dawud often commented on hadith authenticity after the hadith.
(2) Risalah ilaa Ahl Makkah (Letter to People of Makkah): This is a booklet in which Abu Dawud writes about his method and criteria in his compilation of Sunan Abu Dawud.
(3) Other Hadith books. Also Imam Abu Dawud is a reliable source who related to us rulings from his teacher, the great Imam Ahmed ibn Hanbal, about degree of authenticity of Hadith and its chains.
Born: 209 AH (c. 824 CE) in Tirmidh (a city on the banks of the Oxus (Jayhun) River. Tirmidh is in present day Uzbekistan.
Died: {13 Rajab} 279 AH (c. 9 October 892 CE) in Tirmidh (aged 70 years). Lived during the period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full Name: Abu Esa Muhammed ibn Esa ibn Saurah as-Sulami at-Tirmidhi.
Brief Bio:
Imam Tirmidhi also travelled extensively to collect hadith from its narrators. Among places he travelled to for hadith include Hijaz, Iraq and Khorasan. Tirmidhi was a student of the great Imam Bukhari and related many rulings and classifications of hadith and their chains and narrators from Bukhari.
Major Works:
(1) Sunan Tirmidhi: Known also as Jami at-Tirmidhi, this is one of the six most renowned compilations of hadith. It is divided contains about 3956 Hadith with repetitions organised into 46 chapters and sub-sections. Imam Tirmidhi organised the hadith in chapters and placed chapter headings with points related to the hadith in the chapter. He did not intend to collect only authentic hadith of the highest rank, but to collect hadith that are not baseless. As a result, Imam Tirmidhi himself followed up a hadith with his classification of the level of authenticity of that hadith, presence or absence of other narrations of the same hadith, sometimes related comments that Imam Bukhari made about that hadith or its narrator's authenticity and often mentioned fiqh aspects of the hadith in terms of which and how many of the great Scholars of that or earlier generations held a particular fiqh ruling derived from that hadith. Moreover, Imam Tirmidhi also used a classification of authenticity called Hasan Hadith in a specific manner. Like the other three compilations of hadith, the Sunan Tirmidhi is a treasure not only of hadith but of extra benefits that are unique to it.
(2) Shamail Tirmidhi: Hadith that describe the physical nature and other characteristics of the Prophet Muhammed.
(3) Other books on Hadith.
Born: 215 AH {or 214 AH (c. 829 CE)} in Nasa, in Khorasan, present day Turkmenistan.
Died: 303 AH (c. 915 CE) in ar-Ramlah in Palestine {or Makkah?} (aged 88 years). Lived during the period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full Name: Abu Abdurahman Ahmed ibn Shubaib ibn Ali an-Nasa'ee.
Brief Bio:
Imam Nasa'ee travelled extensively in pursuit of Hadith, including to Hijaz, Khorasan, Shaam (Syria), Mesopotamia (Iraq) and Egypt wherein he stayed for a long time. Imam Nasa'ee faced some trails and hardships from the people in Damascus, as did numerous other great Scholars. Imam Nasaee was one of the authoritative Scholars who commented on authenticity of narrators of hadith, though not to the level of Imam Bukhari and Imam Ahmed ibn Hanbal.
Major Works:
(1) Sunan an-Nasa'ee (as-Sunan as-Sughraa): One of the six most reliable renowned compilations of hadith. The Sunan Nasaee contains about 5758 hadith in 51 chapters. Imam Nasaee did not make this a book only of authentic hadith, but collected hadith that are usable either independently or along with other hadith, like the four of the six books of Sunan. Hence, Imam Nasa'ee often mentioned rank of a hadith's authenticity and even rank of some narrators or aspects of chain of hadith.
(2) Other important books on hadith matters including as-Sunan al-Kubras and other books.
Born: 209 AH (c. 824 CE) in Qazwin (Qazvin), Persia, in present day Iran.
Died: 273 AH (c. 887 CE) in Qazwin (aged 64 years). Lived during the period of the Abbasid Khilafah.
Full Name: Abu Abdullah Muhammed ibn Yazid ibn Abdullah ibn Majah ar-Rib'ee al-Qazwini.
Brief Bio:
Like the other five, Imam Ibn Majah was a great Scholar not only of Hadith but of Islam on the whole. Like other great Scholars of Hadith of those days, Ibn Majah travelled extensively in pursuit of Hadith, including to ar-Reyy, Basrah, Kufah, Baghdad, Shaam (Syria), Egypt and Hijaz.
Major Works:
(1) Sunan Ibn Majah: One of the six most renowned books and compilations of hadith and often ranked the sixth of the six renowned compilations. It contains about 4341 hadith organised into 37 Chapters and Sub-Sections. Imam Ibn Majah compiled hadith to do with all aspects of Islam along with lot of emphasis on Sunnah and the Islamic belief. The Book begins with a large Chapter on Sunnah (Islamic Beliefs), followed by many Fiqh and other Chapters and ends with a beautiful long and inspiring Chapter on Zuhd (Asceticism). Imam Ibn Majah did not intend this to contain only the authentic hadith but like the other three books of Sunan this contains hadith of lesser authenticity that may be used along with supporting narrations.
(2) Other books on Islam.
--------- --------------- ---------------- ----------